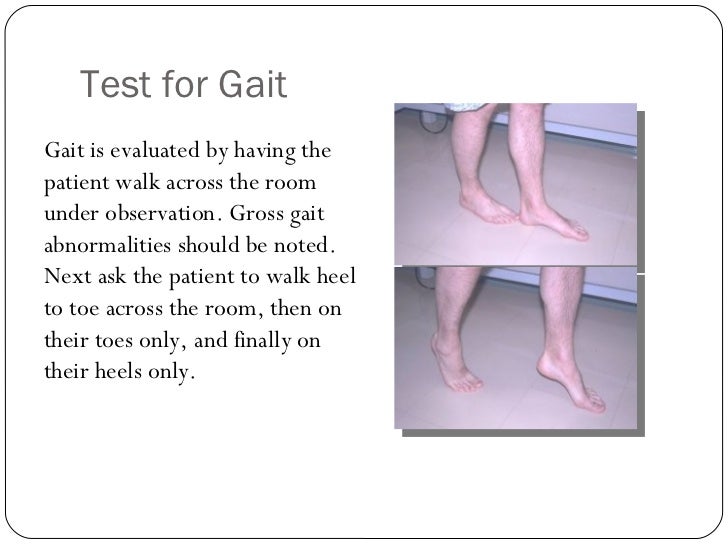
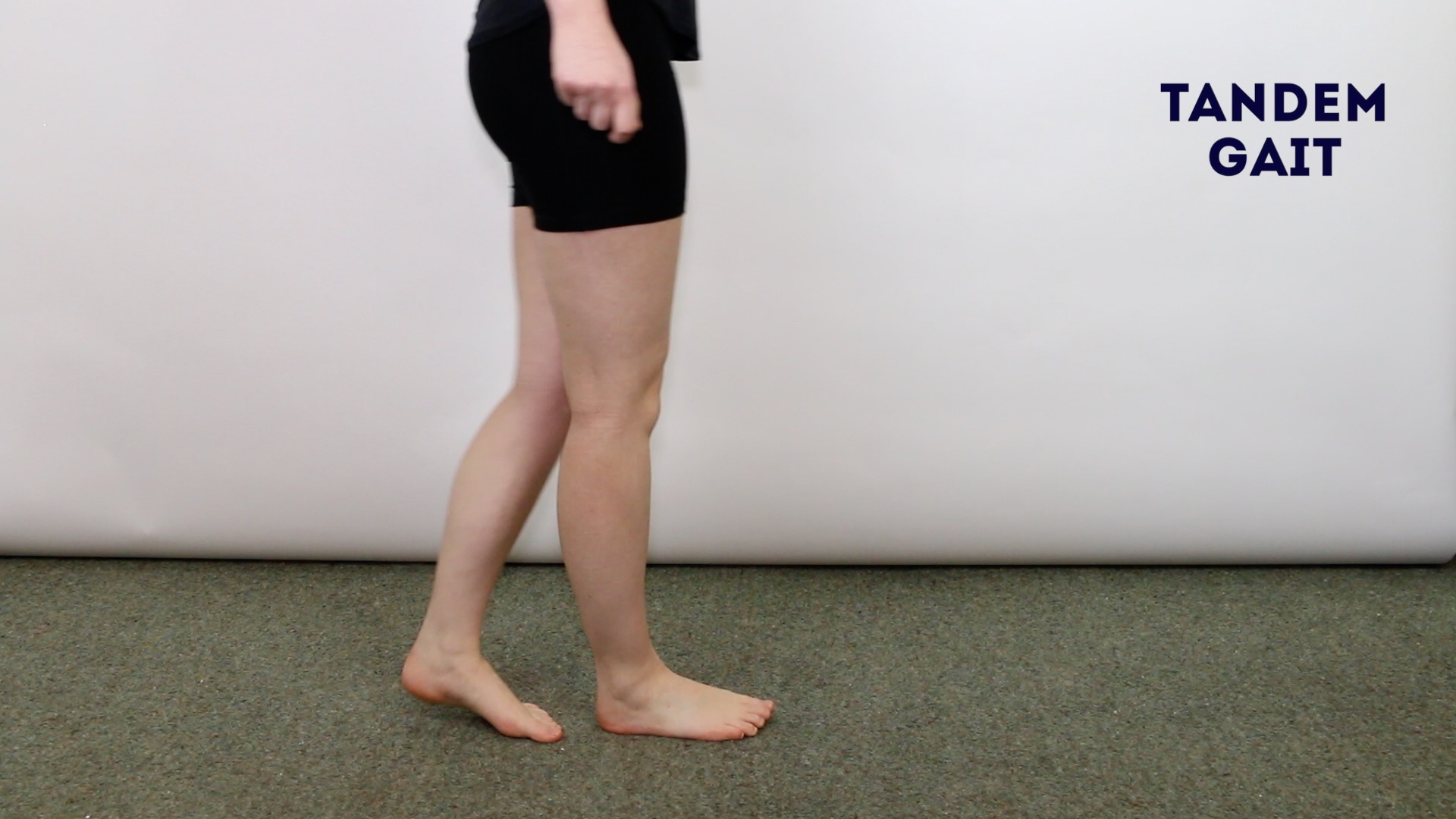
Positive Test. Observing any loss of balance, difficulty of walking in tandem (walking in a straight line) or standing in tandem (standing on 2 feet). Note that standing will be more difficult. Interpretation. Inability to do the above suggests possible cerebral/intracranial lesion.. Tandem gait and the Romberg test are key tests for balance. To test tandem gait, the patient is instructed to walk placing one foot directly in front of the other, heel-to-toe. Normal patients are able to walk without swaying. The Romberg rest is simply tandem walking that is done with the eyes closed and this is done when tandem walking is normal.

(PDF) Tandem walking as a quick screening test for vestibular disorders Tandem Walking for

Building Balance through Strength Training Infinity Health

Tandem Walking Gross Motor and Mobility Activities for Home

Tandem Gait Test

Neuro Assessment

Tandem Walk Vissco Healthcare Private Limited.
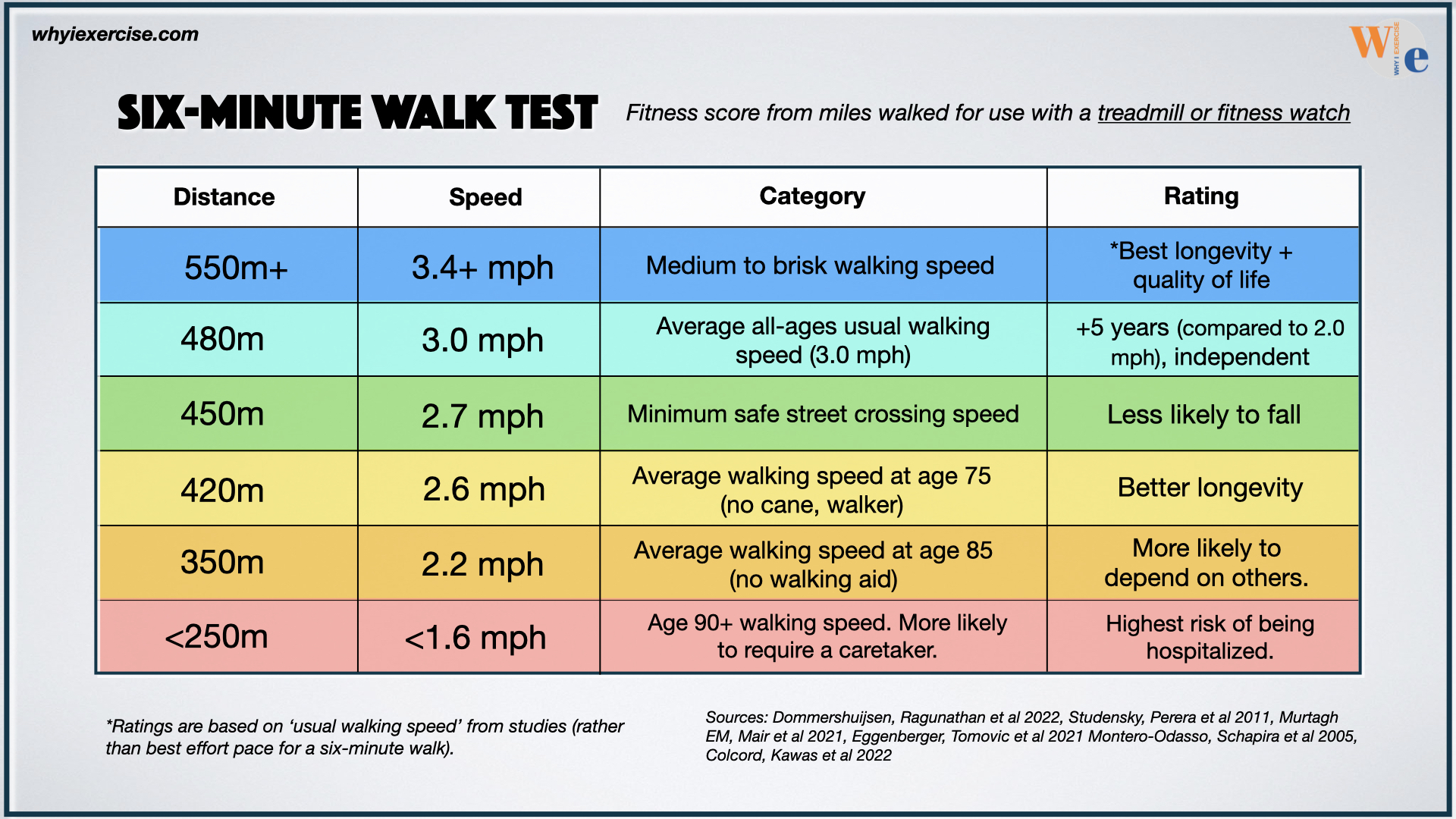
Walking speed for seniors This is a lifesaver!
Coordination, Balance, Gait and Posture

Tandem Gait Test
Cerebellar examination OSCE Guide Geeky Medics
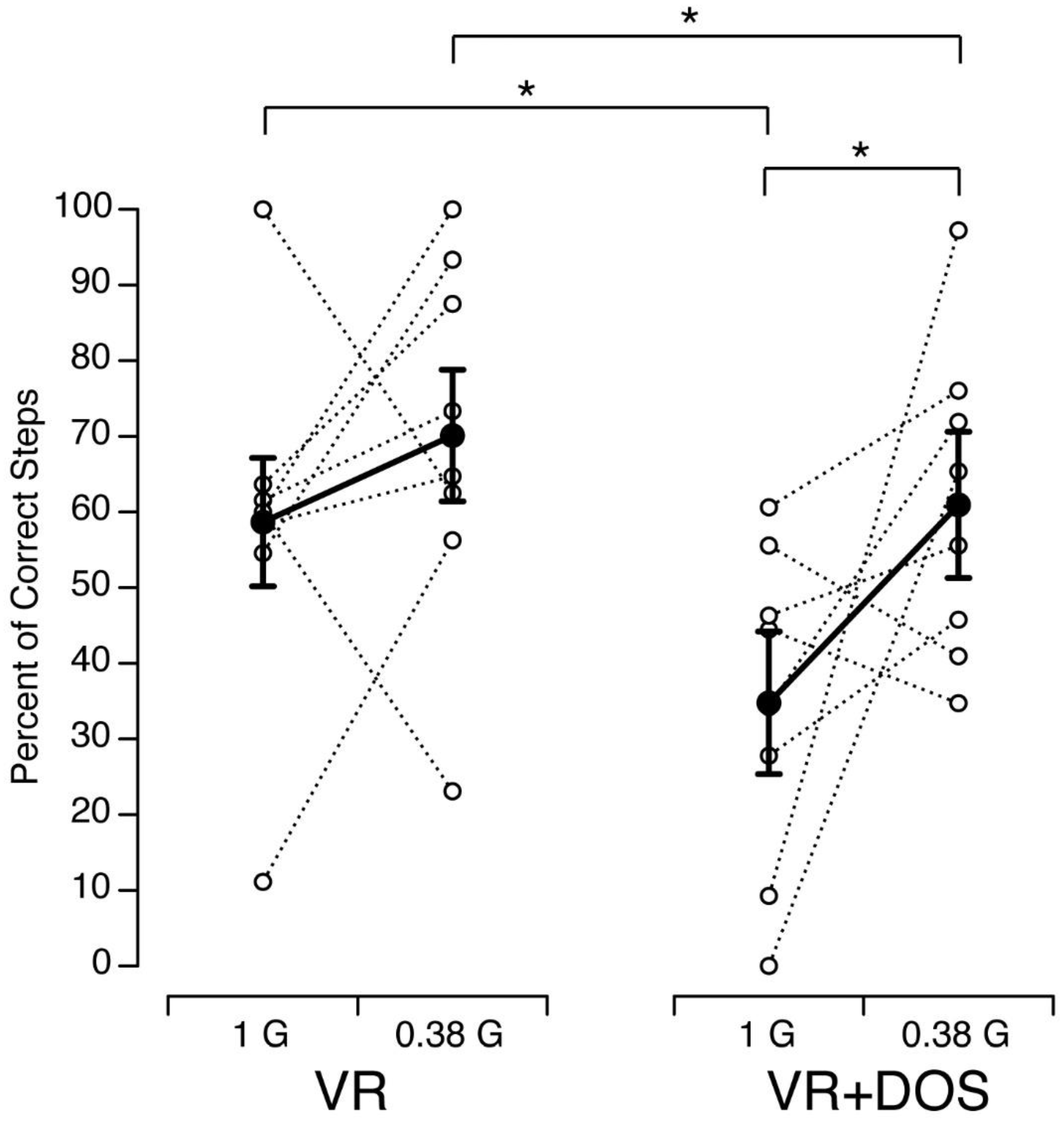
Brain Sciences Free FullText Tandem Walk in Simulated Martian Gravity and Visual Environment

SPPB TEST Tandem, Ergothérapie, Equilibre

(PDF) Tandem walking as a quick screening test for vestibular disorders Tandem Walking for

How to perform the Tandem Walking Physitrack

Tandem Walk YouTube

(PDF) Sharpening the Tandem Walking Test for Screening Peripheral Neuropathy

Lower Limb Neurological Examination OSCE Guide Geeky Medics

The 10 Best Balance Exercises For Seniors — More Life Health Seniors Health & Fitness
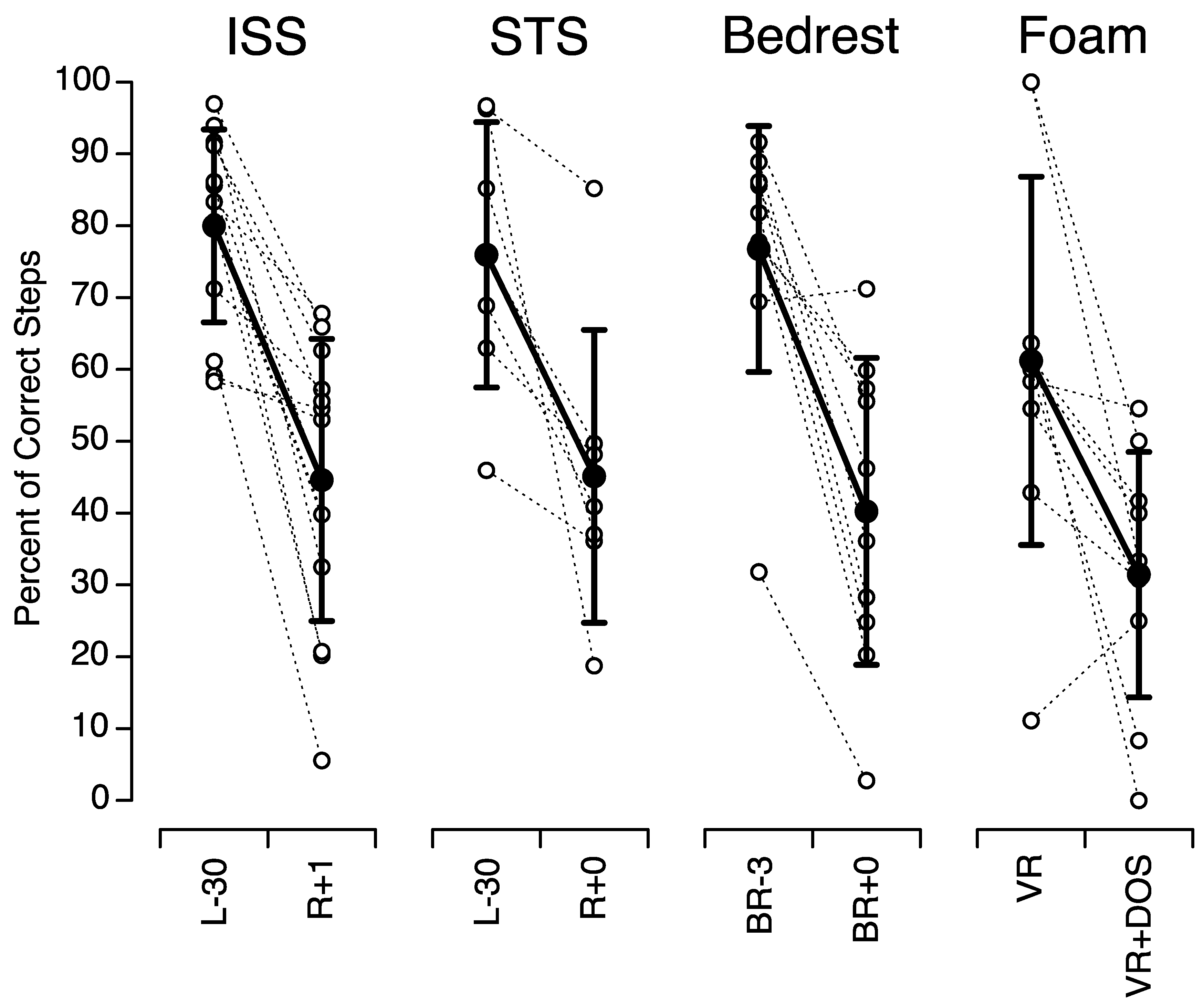
Brain Sciences Free FullText Tandem Walk in Simulated Martian Gravity and Visual Environment

Tandem Gait Test
Conclusion. The heel-to-toe walking test, or tandem gait test, is a simple yet effective clinical examination used to assess a patient’s gait, balance, and coordination. It has wide-ranging applications in medical and law enforcement settings, including evaluating cerebellar diseases, vestibular disorders, and intoxication.. For the single-task tandem gait test, a cut-point of 16 s provided 87.5% sensitivity and 72.4% specificity and correctly classified 82.4% of patients as concussed or control. For the dual-task tandem gait test, a cut-point of 22 s provided 84.8% sensitivity and 72.4% specificity and correctly classified 80.6% of patients as concussed or control.